Is Melatonin Safe for Americans Working Night Shifts?
Dr JK Avhad MBBS MD [ Last updated 13.12.2025 ]
Millions of Americans—nurses, police officers, truck drivers, factory employees, IT engineers, security guards, hotel staff, and emergency responders—work through the night and sleep during the day. This schedule disrupts their circadian rhythm, causing insomnia, fatigue, depression, and chronic sleep deprivation. Because of this, melatonin supplements have become one of the most commonly used sleep aids in the USA.
What Is Melatonin and How Does It Affect Night Shift Workers?
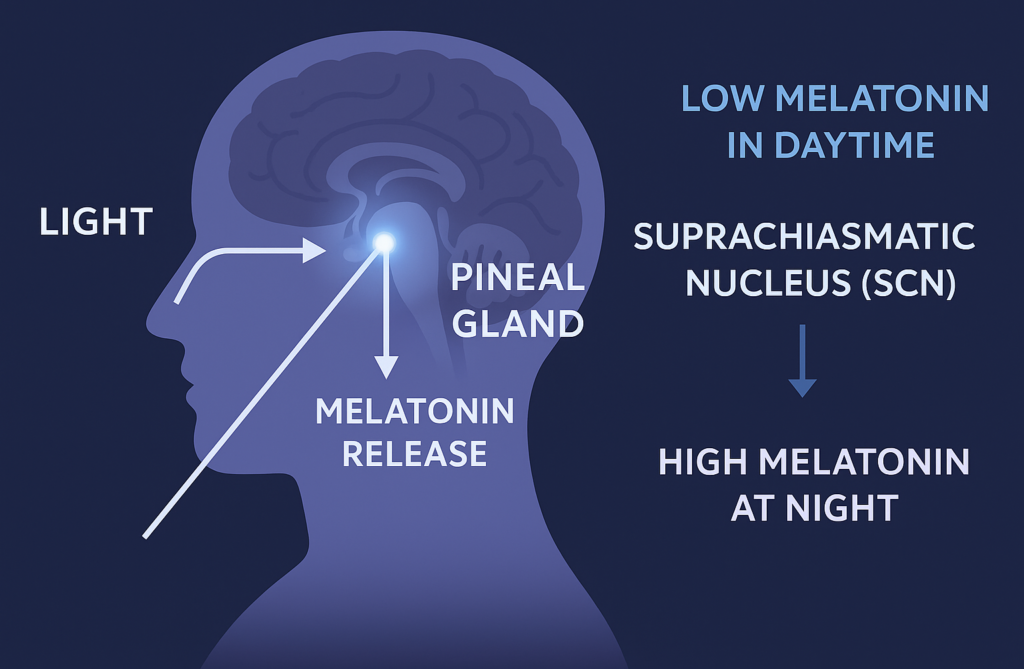
Melatonin is a naturally occurring hormone released by the pineal gland at night. It tells the body it’s time to sleep.
However, night shift workers often sleep during daylight hours, when melatonin production is at its lowest.
This leads to:
- Difficulty falling asleep
- Fragmented daytime sleep
- Low REM sleep
- Chronic fatigue
- Circadian misalignment
The CDC notes that shift workers are at higher risk of sleep disorders because daytime sleeping conflicts with internal biological rhythms (CDC Shift Work Report, 2023) [CDC].
Why Do Night Shift Workers in the USA Struggle With Daytime Sleep?
American night shift workers experience multiple disruptions:
- Daylight exposure while driving home
- Household noise in the morning
- Children getting ready for school
- Blue light exposure
- Inconsistent work schedules
- Rotating shift patterns
Research from the Sleep Foundation confirms night shift workers have up to 40% lower daytime melatonin levels, contributing to poor sleep (Sleep Foundation, 2024) [SF].
Is Melatonin Safe for Americans Working Night Shifts?
Yes — melatonin is generally safe for short-term use
Long-term daily use lacks strong safety data
Lower doses (0.5–3 mg) are safest
High doses (>5 mg) can cause grogginess and dependency
The National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH) states melatonin is safe short-term, but more research is needed on continuous long-term use (NCCIH, 2023)
How Does Melatonin Help Night Shift Workers?
Melatonin can:
- Help you fall asleep faster
- Improve daytime sleep quality
- Reduce sleep latency
- Shift or reset your sleep-wake cycle
A Sleep Medicine Reviews meta-analysis found melatonin effective for shift-work sleep disorder and delayed circadian rhythms (Sleep Medicine Review, 2022)
What Is the Best Melatonin Dosage for Night Shift Workers in USA?
According to Harvard Sleep Medicine (Harvard Health, 2023)
- Start with 0.5 mg
- Most adults need 1–3 mg
- Avoid 5–10 mg unless advised by a clinician
Higher doses lead to:
- Morning grogginess
- Hormonal disturbances
- Headaches
- Vivid dreams
Melatonin is not stronger the more you take—low dose often works better for circadian rhythm shifting.
What Is the Best Time for a Night Shift Worker in USA to Take Melatonin?
Take melatonin:
- 30–60 minutes before intended sleep time
- After arriving home and preparing for bed
- With lights dimmed or off
- Avoiding screens after taking it
Taking melatonin on the job or during breaks is unsafe because it induces drowsiness.
Is It Safe to Take Melatonin Daily While Working Night Shift?
Safe for short-term
Long-term daily use lacks safety research
NIH notes melatonin lacks long-term clinical safety trials in adults beyond a few months (NIH ODS, 2023)
Experts recommend:
- Using melatonin only when adjusting between shifts
- Avoiding daily use for years
- Cycling melatonin (e.g., 5 days on, 2 days off)
Common Side Effects of Melatonin in Night Shift Workers
Common symptoms:
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Drowsiness
- Next-day grogginess (“melatonin hangover”)
- Mood irritability
Less common:
- Low blood pressure
- Bad dreams
- Reduced alertness
- Hormonal effects with long-term use
Cleveland Clinic states melatonin may cause daytime sleepiness and impair reaction time (Cleveland Clinic, 2023)
Is Melatonin Safe for Night Shift Nurses and Healthcare Workers in USA?
For nurses and medical staff:
- Melatonin helps sleep
- But excessive dose may cause impaired alertness during duty
- Long-lasting grogginess may affect patient safety
Recommendation:
- Use 0.5–1 mg, not high doses
- Avoid melatonin close to the next shift
- Allow 8–9 hours between melatonin and duty
Is Melatonin Safe for USA Truck Drivers Working Overnight?
Truck drivers should be extremely cautious.
Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration advises drivers to avoid any sedating supplements too close to driving hours (FMCSA, 2022)
Melatonin can:
- Slow reflexes
- Impair cognitive function
- Cause lingering drowsiness
Drivers should:
- Only take melatonin off-duty
- Ensure at least 8–10 hours before their next drive.
Can Melatonin Reset the Circadian Rhythm for Night Shift Workers?
Yes. Melatonin is scientifically proven to help shift or advance circadian rhythms.
Research shows melatonin shifts the internal clock by about 1 hour per dose when timed correctly (SMR Review, 2022).
Early Signs Melatonin Is Not Safe or Not Working for You
Red flags include:
- Increased anxiety
- Brain fog
- Reliance on higher doses
- Feeling dizzy after waking
- Vivid or disturbing dreams
- Feeling “drugged” after sleep
- Heart palpitations
Stop or reduce dose if these occur.
Who Should NOT Take Melatonin While Working Night Shift?
Avoid melatonin if you:
- Are pregnant or breastfeeding
- Have autoimmune disorders
- Take blood thinners (warfarin)
- Take blood pressure medications
- Take antidepressants
- Experience regular dizziness
- Have epilepsy
- Have hormonal disorders
Always consult a clinician in these cases.
Does Melatonin Interact With Medications Commonly Used by Night Shift Workers?
Possible interactions:
- Antihypertensives
- Antidepressants
- Blood thinners
- Diabetes medications
- Immunosuppressants
NIH lists these as potential interactions (NIH, 2023).
Natural Alternatives to Melatonin for American Night Shift Workers
Evidence-based options include:
Bright Light Therapy
Harvard Sleep Medicine recommends bright-light exposure before the shift to signal wakefulness.
Magnesium Glycinate
Helps relax muscles and improve sleep quality.
Valerian Root
Shown to reduce sleep latency.
Chamomile / Lemon Balm
Natural calming herbs.
Ashwagandha
Shown to reduce cortisol and stress.
Blackout Curtains and White Noise
Improves daytime sleep tremendously.
Cold Bedroom
Ideal temperature: 65°F (18°C) (Sleep Foundation, 2024).
How Should Night Shift Workers Use Melatonin Safely?
Follow These Guidelines:
- Start with 0.5 mg
- Take it 30–60 minutes before sleep
- Avoid screens after taking it
- Avoid high doses
- Don’t mix with alcohol
- Don’t drive or operate machinery
- Don’t take during your shift
- Cycle melatonin use—avoid daily 365-day use
Sample Melatonin Schedule for Night Shift Workers
If shift ends at 6:00 am:
- Reach home: 7:00 am
- Darken environment
- Take 0.5–1 mg melatonin at 7:15 am
- Sleep by 8:00 am
If rotating shifts:
Use melatonin only on transition days (e.g., moving from night to day schedule).
Long-Term Safety: Should Night Shift Workers Depend on Melatonin?
Current research lacks long-term (multi-year) studies.
Experts caution:
- Possible hormonal disruption
- Dependence
- Reduced natural melatonin production
Thus, experts prefer using melatonin only temporarily or intermittently.
Conclusion: Is Melatonin Safe for Americans Working Night Shifts?
Yes, melatonin is safe short-term
Low dose (0.5–3 mg) recommended
Avoid high doses
Not enough evidence for long-term daily use
Best used during shift transitions
Must avoid before driving or operating machinery
For most American night shift workers, melatonin is a helpful tool, not a permanent solution.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. How much melatonin should night shift workers take?
Most adults should take 0.5–3 mg (Harvard Health, 2023).
Q. Can you take melatonin every morning after a night shift?
Yes short-term, but avoid long-term continuous use because safety data is limited (NIH, 2023).
Q. Is 10 mg melatonin safe for shift workers?
No. High doses can cause grogginess and slow reflexes.
Q. How long does melatonin last?
Melatonin’s effects last 4–8 hours.
Q. Can melatonin cause morning anxiety for night shift workers?
Yes. Some workers experience rebound alertness or cortisol spikes.
Q. Can melatonin help reset sleep-wake cycles?
Yes, when timed properly, melatonin can shift circadian rhythms by 1 hour.
Q. What is the safest melatonin for night shift workers?
Low-dose (0.5–1 mg) sublingual or immediate-release tablets.
This article is for informational purpose only and does not substitute for professional medical advise. For proper diagnosis and treatment seek the help of your healthcare provider.
